Blog Details
Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA)
By Dr. Sakshi Bansal / 10 Feb 2024Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles of men who have difficulties producing sperm or have obstructive azoospermia. This report aims to provide an overview of TESA, its procedure, indications, risks, and outcomes.
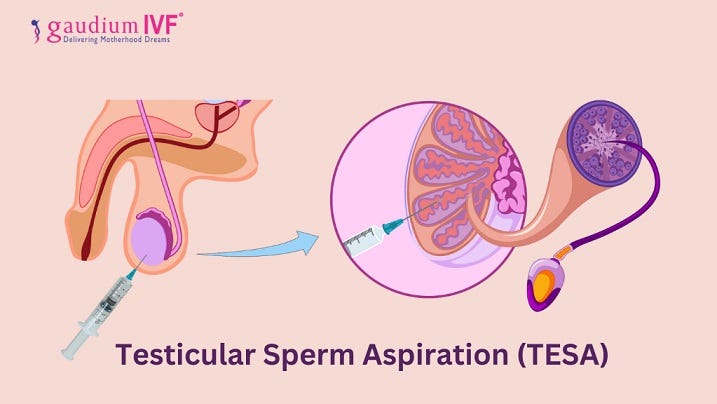
Procedure:Anesthesia: TESA is typically performed under local anesthesia to numb the area.
Sperm Retrieval: A fine needle is inserted into the testicle, and tissue or fluid is aspirated from the testicular parenchyma.
Sperm Analysis: The retrieved material is examined under a microscope to isolate viable sperm for further use in assisted reproductive techniques (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Indications for TESA:- Azoospermia (absence of sperm in ejaculate)
- Non-obstructive azoospermia (testicular failure)
- Obstructive azoospermia (blockage preventing sperm from reaching the ejaculate)
Risks and Complications:1. Discomfort: Patients may experience discomfort or pain during or after the procedure.
2. Bleeding: Minimal bleeding at the aspiration site is possible.
3. Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the site of needle insertion.
4. Failure to Retrieve Sperm: In some cases, TESA may not yield sufficient sperm for use in ART procedures.
Conclusion:Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) is a valuable technique for retrieving sperm in men with various forms of azoospermia. While it carries minimal risks, its potential to enable biological parenthood through assisted reproductive techniques underscores its importance in infertility treatment.
Note: Patients undergoing TESA should receive thorough counseling regarding the procedure, its risks, and potential outcomes, and should be under the care of a qualified reproductive specialist.
 Dr. Sakshi Bansal
Dr. Sakshi Bansal